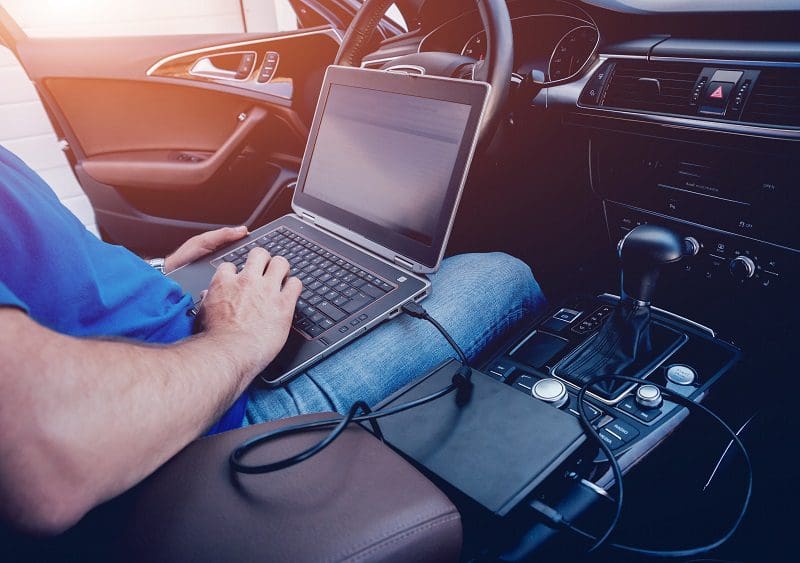
Unlike buying and setting up a basic home audio system, having a new amplifier and speakers installed in your car or truck requires proper setup and tuning. At home, you can adjust the placement of the speakers and how much they are toed in to affect the focus of the soundstage and the bass response. In a car, your installer needs to mount the amplifier, wire it, then adjust the crossover and sensitivity controls to work with your source unit and the design of the system. Getting these settings wrong can have an audibly detrimental effect on the performance of your mobile audio system. Let’s look at why proper amplifier setup and tuning are so important.
Unlike buying and setting up a basic home audio system, having a new amplifier and speakers installed in your car or truck requires proper setup and tuning. At home, you can adjust the placement of the speakers and how much they are toed in to affect the focus of the soundstage and the bass response. In a car, your installer needs to mount the amplifier, wire it, then adjust the crossover and sensitivity controls to work with your source unit and the design of the system. Getting these settings wrong can have an audibly detrimental effect on the performance of your mobile audio system. Let’s look at why proper amplifier setup and tuning are so important.
Basic Car Audio Amplifier Setup
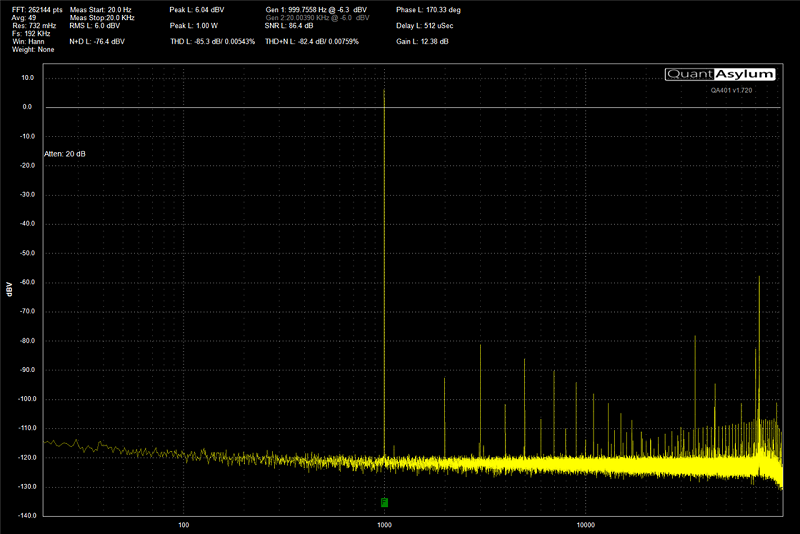
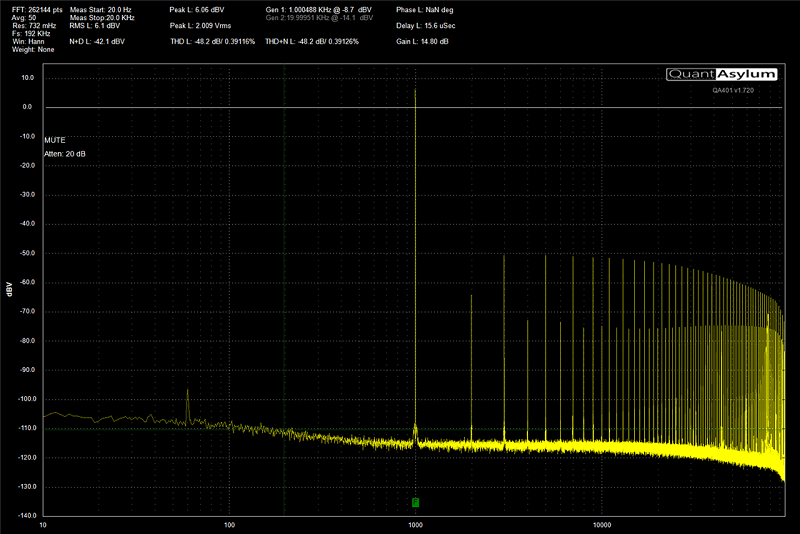
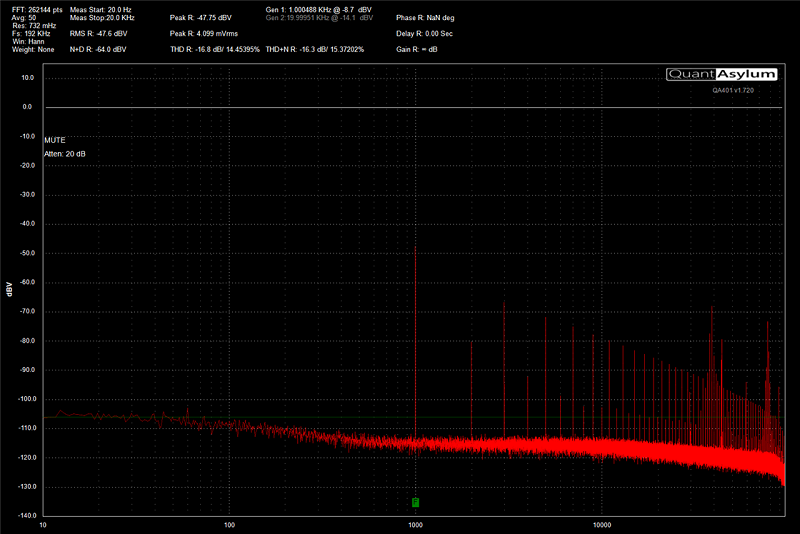
 Once the power, ground and remote turn-on connections are made, and new speaker wires have been run to each location in the car, the last step is to connect your amplifier to the source unit in the system. Depending on the design of your audio system, you may have a very basic CD player with low-voltage preamp outputs, a premium multimedia receiver with 5-volt preamp outputs or you might be using a factory radio with or without an amplifier. The sensitivity (gain) control on your amplifier exists to ensure that your new amp can reach its full potential from any of these sources. Many shops use an oscilloscope or a distortion detecting device to ensure that the system is configured accurately and efficiently.
Once the power, ground and remote turn-on connections are made, and new speaker wires have been run to each location in the car, the last step is to connect your amplifier to the source unit in the system. Depending on the design of your audio system, you may have a very basic CD player with low-voltage preamp outputs, a premium multimedia receiver with 5-volt preamp outputs or you might be using a factory radio with or without an amplifier. The sensitivity (gain) control on your amplifier exists to ensure that your new amp can reach its full potential from any of these sources. Many shops use an oscilloscope or a distortion detecting device to ensure that the system is configured accurately and efficiently.
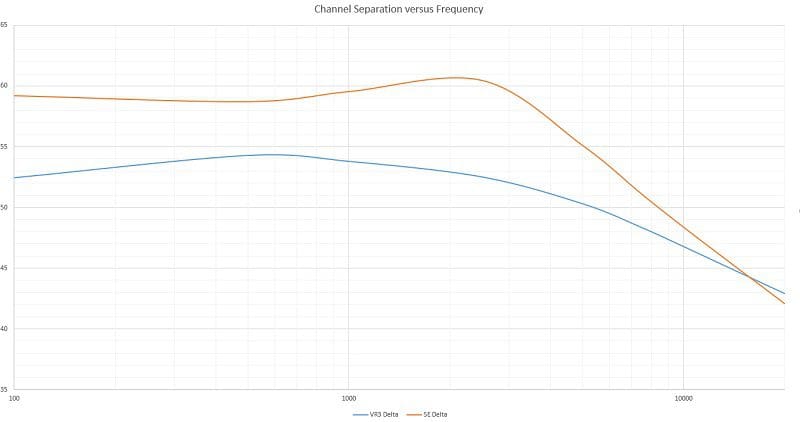
 If you are adding a subwoofer to your vehicle, the basic process is the same, but your installer now has to balance the output of the sub to the other speakers in the car. He or she will also have to set the crossovers on the amp so that the output of the sub blends with the output of the smaller speakers. Many high-end shops use a real-time analyzer (RTA) to perform this task to ensure the output of the speakers blends perfectly. Setting up crossovers also needs to take into account the physical capabilities of a speaker. A small 4-inch midrange certainly can’t produce the same amount of low-frequency information as a 6.5-inch woofer and needs to be adjusted accordingly.
If you are adding a subwoofer to your vehicle, the basic process is the same, but your installer now has to balance the output of the sub to the other speakers in the car. He or she will also have to set the crossovers on the amp so that the output of the sub blends with the output of the smaller speakers. Many high-end shops use a real-time analyzer (RTA) to perform this task to ensure the output of the speakers blends perfectly. Setting up crossovers also needs to take into account the physical capabilities of a speaker. A small 4-inch midrange certainly can’t produce the same amount of low-frequency information as a 6.5-inch woofer and needs to be adjusted accordingly.
What if Things Aren’t Set Up Properly?
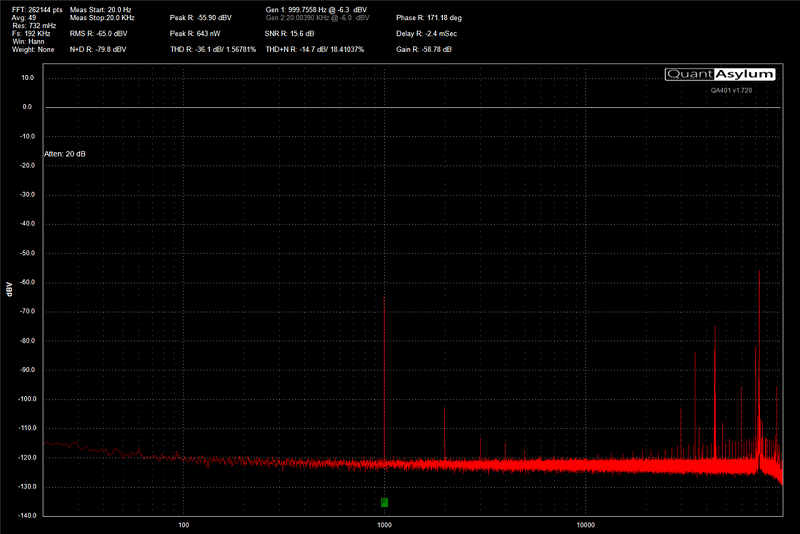
 If the sensitivity setting is wrong, you may experience a lot of background noise or hiss in your system. At the opposite end of the scale, you may not be able to reach full volume. If the crossovers aren’t right, you run the risk of damage to small speakers or experience unwanted dips and peaks in the frequency response of the system around the crossover point.
If the sensitivity setting is wrong, you may experience a lot of background noise or hiss in your system. At the opposite end of the scale, you may not be able to reach full volume. If the crossovers aren’t right, you run the risk of damage to small speakers or experience unwanted dips and peaks in the frequency response of the system around the crossover point.
Setting Up a Digital Signal Processor
 The goal of adding a digital signal processor (DSP) to a mobile audio system is to produce accurate imaging and realistic frequency response at the listening position. Setting up a DSP properly requires training and an investment in tools. Beyond that, your installer needs to use a real-time analyzer to measure the acoustic performance of the system. While there are a variety of processes used to set parameters like signal delay and different theories on whether to boost or cut EQ bands, the person tuning the system needs to have a full and detailed understanding of how the adjustments he or she makes affect the amplifiers, the speakers and the resulting acoustic performance of the system.
The goal of adding a digital signal processor (DSP) to a mobile audio system is to produce accurate imaging and realistic frequency response at the listening position. Setting up a DSP properly requires training and an investment in tools. Beyond that, your installer needs to use a real-time analyzer to measure the acoustic performance of the system. While there are a variety of processes used to set parameters like signal delay and different theories on whether to boost or cut EQ bands, the person tuning the system needs to have a full and detailed understanding of how the adjustments he or she makes affect the amplifiers, the speakers and the resulting acoustic performance of the system.
What if Your DSP Isn’t Set Up Properly?
In the simplest of scenarios, your audio system may not be as optimized as it could be. There may still be frequency response, imaging or staging issues. If the settings are really far off, you run the risk of damaging speakers permanently, or the performance of your sound system might have been better off with no processing at all.
Choosing the Right Retailer to Setup Your Mobile Audio System
 The easiest way to choose a shop to set up your mobile audio system is to ask to listen to one of their demo vehicles. If you like the sound of the system, it offers excellent imaging and staging and plays at a volume level that suits your listening preferences, they should be qualified to recreate something very similar in your vehicle. If you aren’t happy with the way the vehicle sounds, ask to listen to a client vehicle. If you still aren’t satisfied, look for another shop to work on your car or truck.
The easiest way to choose a shop to set up your mobile audio system is to ask to listen to one of their demo vehicles. If you like the sound of the system, it offers excellent imaging and staging and plays at a volume level that suits your listening preferences, they should be qualified to recreate something very similar in your vehicle. If you aren’t happy with the way the vehicle sounds, ask to listen to a client vehicle. If you still aren’t satisfied, look for another shop to work on your car or truck.
When a car audio system is set up and tuned properly, it can rival some of the best home audio and studio reference systems on the planet. Don’t short yourself on getting the most performance possible from your upgrade – make sure it’s installed and configured properly.
This article is written and produced by the team at www.BestCarAudio.com. Reproduction or use of any kind is prohibited without the express written permission of 1sixty8 media.