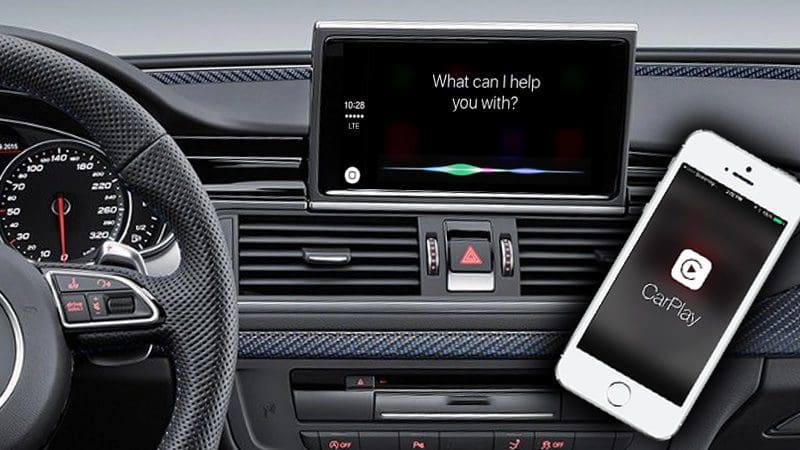
 Apple CarPlay and Android Auto smartphone integration systems are extremely popular features found in aftermarket source units from all the key brands. The technology behind CarPlay and Android Auto continue to evolve, and in the summer of 2017, the aftermarket industry saw the introduction of wireless CarPlay connectivity. Android followed suit in 2018 with a comparable solution that didn’t require cables. Let’s take a look at how wireless smartphone integration works and why it might be the perfect solution for the busy road warrior.
Apple CarPlay and Android Auto smartphone integration systems are extremely popular features found in aftermarket source units from all the key brands. The technology behind CarPlay and Android Auto continue to evolve, and in the summer of 2017, the aftermarket industry saw the introduction of wireless CarPlay connectivity. Android followed suit in 2018 with a comparable solution that didn’t require cables. Let’s take a look at how wireless smartphone integration works and why it might be the perfect solution for the busy road warrior.
How Do CarPlay and Android Auto Work?
 These infotainment solutions require two components to provide you with Internet-connected voice recognition access to your music, navigation and communication functions. First and foremost, the source unit in the vehicle needs to have the software built in. Including CarPlay and Android Auto in a multimedia receiver is a massive undertaking for a radio manufacturer. More so on the Apple side, because there are very strict and specific requirements for display size, interface design, processor speed and hardware components. The goal is to ensure that the experience for you, the consumer, is a good one. It can take several years of design, testing and approvals to bring a new radio model to market.
These infotainment solutions require two components to provide you with Internet-connected voice recognition access to your music, navigation and communication functions. First and foremost, the source unit in the vehicle needs to have the software built in. Including CarPlay and Android Auto in a multimedia receiver is a massive undertaking for a radio manufacturer. More so on the Apple side, because there are very strict and specific requirements for display size, interface design, processor speed and hardware components. The goal is to ensure that the experience for you, the consumer, is a good one. It can take several years of design, testing and approvals to bring a new radio model to market.
When you want to make a phone call or pick music to enjoy, you activate the voice recognition function on your radio and verbally request what you want. The radio will relay a digital recording of your request to the Apple or Google voice recognition servers using your phone’s Internet connection. The server will analyze the message and translate that into a command or sequence of commands that are sent back to your phone. Your phone will execute the command and display the outcome on your radio.
 Up until recently, the connection between your phone and the radio for CarPlay and Android Auto has used a USB cable. With the introduction of wireless connectivity, things have changed. A Wi-Fi connection between your source unit and your smartphone replaces the wired connection for reliable, high-speed communication. Initially, a little more setup is required to get your smartphone and radio talking, but once configured, everything operates intuitively.
Up until recently, the connection between your phone and the radio for CarPlay and Android Auto has used a USB cable. With the introduction of wireless connectivity, things have changed. A Wi-Fi connection between your source unit and your smartphone replaces the wired connection for reliable, high-speed communication. Initially, a little more setup is required to get your smartphone and radio talking, but once configured, everything operates intuitively.
Wireless Apple CarPlay
Contrary to some reports that claim wireless CarPlay started with iOS 9, this functionality launched with the introduction of iOS 8.3 in April 2015. It was several years before anyone had a viable and tested application on the road. Remember our comment about development and testing time?
Wireless Android Auto
 In November 2017, Google announced the ability for devices running Android to run Android Auto as a stand-alone app without the need for an aftermarket source unit. At CES 2018, several aftermarket manufacturers announced they would include wireless Android Auto connectivity on their new source units.
In November 2017, Google announced the ability for devices running Android to run Android Auto as a stand-alone app without the need for an aftermarket source unit. At CES 2018, several aftermarket manufacturers announced they would include wireless Android Auto connectivity on their new source units.
At the time of launch, only smartphones from Google themselves would work with wireless Android Auto. These phones include the first- and second-generation Google Pixel and Pixel 2, the Nexus 5X and the Nexus 5P. Rumors began circulating in the summer of 2018 that some devices running the Oreo version of the Android operating system (Android 8.1) may become compatible with wireless Android Auto in the future. These rumors also include speculation that devices running Android P (the next version of Android, presumably called Android 9) will support wireless connectivity with more devices.
Do You Need Wireless Smartphone Connectivity?
 There are have been many discussions about the benefits and drawbacks of wireless connectivity. The biggest point of debate is around phone charging. In most cases, drivers take advantage of the ability to charge their phones when they get in their vehicles as they travel. For most people, this requires that the USB cable is connected to their phone. With that said, the Apple iPhone 8, 8 Plus and X include wireless charging. On the Android side, recent devices from Samsung, LG, Google, Microsoft and Blackberry include wireless charging.
There are have been many discussions about the benefits and drawbacks of wireless connectivity. The biggest point of debate is around phone charging. In most cases, drivers take advantage of the ability to charge their phones when they get in their vehicles as they travel. For most people, this requires that the USB cable is connected to their phone. With that said, the Apple iPhone 8, 8 Plus and X include wireless charging. On the Android side, recent devices from Samsung, LG, Google, Microsoft and Blackberry include wireless charging.
 Flipping back to the cons side of the debate, you need a wireless charging base in your vehicle to take advantage of the wireless charging feature. Vehicles from Audi, BMW, Chrysler, Ford, Honda, Mercedes-Benz, Toyota, Volkswagen and Volvo include Qi compatible charging solutions. Qi is the standard for wireless charging for Apple devices.
Flipping back to the cons side of the debate, you need a wireless charging base in your vehicle to take advantage of the wireless charging feature. Vehicles from Audi, BMW, Chrysler, Ford, Honda, Mercedes-Benz, Toyota, Volkswagen and Volvo include Qi compatible charging solutions. Qi is the standard for wireless charging for Apple devices.
Don’t fret: Several aftermarket suppliers, including Scosche, Belkin, Autoleads and Brandmotion offer wireless charging solutions that a mobile enhancement retailer can integrate with your vehicle.
A Simple Way to Stay Connected
If you are in and out of your vehicle often during the day, wireless smartphone connectivity, just like Bluetooth, is an ideal solution to get you connected quickly and easily. Without a way to charge your phone, you will want to keep an eye on the battery level, especially on long drives. To find out about the wireless smartphone connectivity and charging options that are available for your car, truck or SUV, drop by your local mobile enhancement retailer today and speak with one of their product experts.
This article is written and produced by the team at www.BestCarAudio.com. Reproduction or use of any kind is prohibited without the express written permission of 1sixty8 media.
 Back over accidents are responsible for more than 200 deaths and 12,000 injuries each year. The US Congress passed a law in 2008 that would enact measures to use technology to prevent accidents like these. After years of delays, the US Department of Transportation finally announced that new cars must come with a backup camera.
Back over accidents are responsible for more than 200 deaths and 12,000 injuries each year. The US Congress passed a law in 2008 that would enact measures to use technology to prevent accidents like these. After years of delays, the US Department of Transportation finally announced that new cars must come with a backup camera. In the simplest of terms, a
In the simplest of terms, a  Most factory-installed cameras are mounted above the license plate on a car or in the handle or tailgate emblem of a truck. Aftermarket camera solutions are available to mimic these installation locations. Many vehicles like the Mercedes Sprinter, Ford F-150 and GMC Silverado and Chevy Sierra have aftermarket solutions that look identical to factory offerings. The cameras are water resistant and carry an IP66 (or higher) dust and water intrusion rating. This IP rating means that the cameras can withstand going through the car wash or exposure to the everyday challenges Mother Nature throws their way. Universal cameras are available in surface and flush mount applications. Your mobile enhancement retailer can help you choose the right style for your application.
Most factory-installed cameras are mounted above the license plate on a car or in the handle or tailgate emblem of a truck. Aftermarket camera solutions are available to mimic these installation locations. Many vehicles like the Mercedes Sprinter, Ford F-150 and GMC Silverado and Chevy Sierra have aftermarket solutions that look identical to factory offerings. The cameras are water resistant and carry an IP66 (or higher) dust and water intrusion rating. This IP rating means that the cameras can withstand going through the car wash or exposure to the everyday challenges Mother Nature throws their way. Universal cameras are available in surface and flush mount applications. Your mobile enhancement retailer can help you choose the right style for your application. If your car or truck came with a color display for the factory radio or infotainment system, there are many companies that offer premium integration modules that allow the image from the backup camera to be displayed on this screen. Using a factory screen is the most integrated of solutions and truly mimics a factory-installed system.
If your car or truck came with a color display for the factory radio or infotainment system, there are many companies that offer premium integration modules that allow the image from the backup camera to be displayed on this screen. Using a factory screen is the most integrated of solutions and truly mimics a factory-installed system. If your vehicle doesn’t have a color screen, another popular option to display a camera image is a replacement rearview mirror that features an integrated color display. When the camera is not in use, the mirror looks normal and will show you what is happening behind your vehicle. When you put the transmission in reverse, a compact LCD screen shines through the mirrored surface to display the camera image. While typically small in size (around 4 inches diagonally), they work very well and are quite popular.
If your vehicle doesn’t have a color screen, another popular option to display a camera image is a replacement rearview mirror that features an integrated color display. When the camera is not in use, the mirror looks normal and will show you what is happening behind your vehicle. When you put the transmission in reverse, a compact LCD screen shines through the mirrored surface to display the camera image. While typically small in size (around 4 inches diagonally), they work very well and are quite popular. A popular upgrade for older vehicles is to replace the
A popular upgrade for older vehicles is to replace the  If none of the above options suit your application or you require a larger screen, then consider having a stand-alone monitor installed in your vehicle. Commercial applications such as tow trucks, snow plows, garbage trucks, recycling trucks and delivery vehicles often choose a stand-alone monitor. The image is large, and the unit can be placed in a convenient location.
If none of the above options suit your application or you require a larger screen, then consider having a stand-alone monitor installed in your vehicle. Commercial applications such as tow trucks, snow plows, garbage trucks, recycling trucks and delivery vehicles often choose a stand-alone monitor. The image is large, and the unit can be placed in a convenient location. Many luxury vehicles combine a
Many luxury vehicles combine a  Did you know that you can get great sound in your car or truck using your
Did you know that you can get great sound in your car or truck using your  Fewer and fewer cars today have radios that only play music. They show
Fewer and fewer cars today have radios that only play music. They show  In the good old days, factory audio systems included a radio, a simple analog amplifier and speakers. If you had a luxury vehicle, the manufacturer may have opted to include a subwoofer for a little more (but still not enough) bass. The radio was a simple affair with a tuner, CD player, auxiliary input and maybe a USB port and satellite radio connection. The output of the radio either powered the speakers in the car directly or fed a signal to a small amplifier.
In the good old days, factory audio systems included a radio, a simple analog amplifier and speakers. If you had a luxury vehicle, the manufacturer may have opted to include a subwoofer for a little more (but still not enough) bass. The radio was a simple affair with a tuner, CD player, auxiliary input and maybe a USB port and satellite radio connection. The output of the radio either powered the speakers in the car directly or fed a signal to a small amplifier. Let’s look at three common upgrades that mobile electronics retailers across the nation perform every day. Since 2009, the Ford F-150 has come equipped with an amplifier in the back of the truck that includes the master volume control for the system as well as equalization and crossovers for the speakers. Upgrading this popular vehicle required summing audio signals coming out of the amp back together and removing signal processing.
Let’s look at three common upgrades that mobile electronics retailers across the nation perform every day. Since 2009, the Ford F-150 has come equipped with an amplifier in the back of the truck that includes the master volume control for the system as well as equalization and crossovers for the speakers. Upgrading this popular vehicle required summing audio signals coming out of the amp back together and removing signal processing. Another popular audio system upgrade interface is the iDatalink Maestro DSR1. Automotive Data Solutions partnered with the audio experts at Rockford Fosgate to develop this interface and tuning solution. ADS are experts in the field of CAN communication protocols, thanks to their experience with remote car starter integration modules.
Another popular audio system upgrade interface is the iDatalink Maestro DSR1. Automotive Data Solutions partnered with the audio experts at Rockford Fosgate to develop this interface and tuning solution. ADS are experts in the field of CAN communication protocols, thanks to their experience with remote car starter integration modules.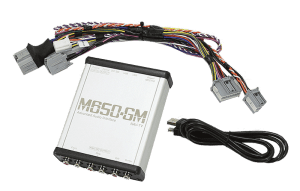 NAV-TV has created an impressive solution that is compatible with Chevy, GMC and Cadillac vehicles with the MyLink and Cue-equipped 4-inch (IO4) and 8-inch (IO5/IO6) source units. This interface connects to the MOST (Media Oriented System Transport) digital signal that runs from the factory radio to the amplifier in these vehicles to extract six channels of full-bandwidth audio that is free from equalization or signal delay.
NAV-TV has created an impressive solution that is compatible with Chevy, GMC and Cadillac vehicles with the MyLink and Cue-equipped 4-inch (IO4) and 8-inch (IO5/IO6) source units. This interface connects to the MOST (Media Oriented System Transport) digital signal that runs from the factory radio to the amplifier in these vehicles to extract six channels of full-bandwidth audio that is free from equalization or signal delay.


 One product that most
One product that most Aftermarket sound deadening products work the same way. Most sound deadening is sold in sheets or rolls. The material is very dense and has one surface that includes a strong adhesive. Your installer can apply the material to flat metal surfaces like the doors, floor, roof, firewall, rear fenders and trunk of your vehicle.
Aftermarket sound deadening products work the same way. Most sound deadening is sold in sheets or rolls. The material is very dense and has one surface that includes a strong adhesive. Your installer can apply the material to flat metal surfaces like the doors, floor, roof, firewall, rear fenders and trunk of your vehicle.
 First, by simply reducing the background noise in your car or truck, you improve the effective signal-to-noise ratio of your stereo. What does this mean? Having less background noise makes it easier for you to hear the quiet parts of your music. Imagine if you were listening to a track at a volume level of 100dB. If you have background noise level of 95 dB, any portion of the song that is around the 95dB level will have to battle with the background noise to be heard. If you can reduce the noise level in your car to 90 dB, you can hear more of your music.
First, by simply reducing the background noise in your car or truck, you improve the effective signal-to-noise ratio of your stereo. What does this mean? Having less background noise makes it easier for you to hear the quiet parts of your music. Imagine if you were listening to a track at a volume level of 100dB. If you have background noise level of 95 dB, any portion of the song that is around the 95dB level will have to battle with the background noise to be heard. If you can reduce the noise level in your car to 90 dB, you can hear more of your music.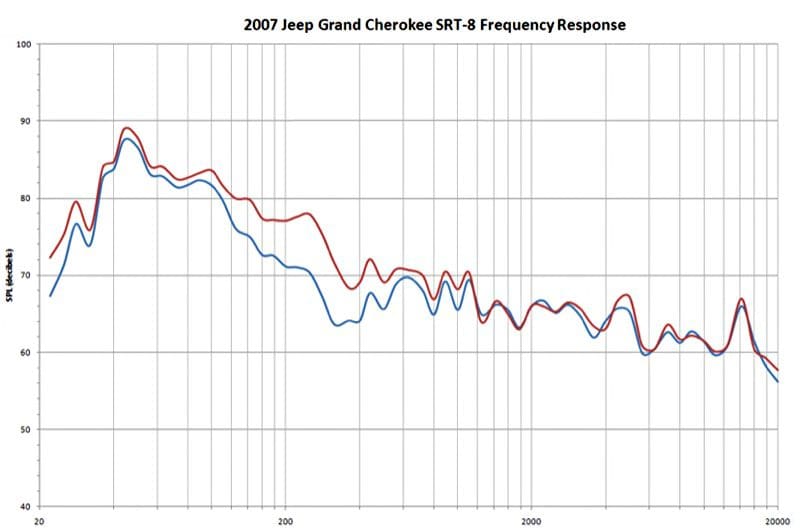
 If you watch TV shows like “Detroit Muscle,” “Truck Tech” or “Overhaulin’,” you’ve undoubtedly seen the guys apply a thorough layer of sound deadening material to the floor of some of the coolest hot rods ever. Not only do these materials help keep your vehicle quiet, but they also help block heat from the road, engine, transmission and exhaust from heating up the interior of your vehicle. Dynaliner from Dynamic Control of North America, D-Mat from Design Engineering and the aptly named Heat Barrier from Thermo-Tec are specifically designed to prevent heat transfer into the interior of your vehicle.
If you watch TV shows like “Detroit Muscle,” “Truck Tech” or “Overhaulin’,” you’ve undoubtedly seen the guys apply a thorough layer of sound deadening material to the floor of some of the coolest hot rods ever. Not only do these materials help keep your vehicle quiet, but they also help block heat from the road, engine, transmission and exhaust from heating up the interior of your vehicle. Dynaliner from Dynamic Control of North America, D-Mat from Design Engineering and the aptly named Heat Barrier from Thermo-Tec are specifically designed to prevent heat transfer into the interior of your vehicle. There are two common problems that occur with damping materials. First, they simply may not have a strong adhesive or they require extensive surface preparation to stay adhered to a panel. Some damping materials will stick to slightly dusty surfaces without any problems. The second and more important concern is that the material itself is thermally stable. You don’t want the deadening to peel off when it gets hot in the summer. We’ve heard of many cases where vehicle carpets and headliners have needed to be replaced because damping materials turned to a liquid and contaminated them.
There are two common problems that occur with damping materials. First, they simply may not have a strong adhesive or they require extensive surface preparation to stay adhered to a panel. Some damping materials will stick to slightly dusty surfaces without any problems. The second and more important concern is that the material itself is thermally stable. You don’t want the deadening to peel off when it gets hot in the summer. We’ve heard of many cases where vehicle carpets and headliners have needed to be replaced because damping materials turned to a liquid and contaminated them.